 |
Washington (AFP) May 4, 2011 Huge objects in the universe distort space and time with the force of their gravity, scientists said Wednesday after a NASA probe confirmed two key parts of Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity. "Einstein survives," chuckled Francis Everitt, Stanford University physicist and principal investigator for Gravity Probe B (GP-B), one of the US space agency's longest running projects. The physics experiment was more than four decades in the making, and finally launched in 2004. "In Einstein's universe, space and time are warped by gravity. The Earth distorts the space around it very slightly by its gravity," he said, explaining the Jewish physicist's theory devised nearly 100 years ago, long before the technology existed to test it. "Imagine the Earth as if it were immersed in honey. As the planet rotates, the honey around it would swirl, and it's the same with space and time," said Everitt. "GP-B confirmed two of the most profound predictions of Einstein's universe, having far-reaching implications across astrophysics research," he said, predicting the mission would "have a lasting legacy on Earth and in space." The satellite carried four advanced gyroscopes to measure geodetic effect, or the warping of space and time around a gravitational body, and frame-dragging, or how much a spinning object pulls space and time with it when it turns. If Einstein's theory were disproved, the "gyroscopes would point in the same direction forever while in orbit," NASA said in a statement. "But in confirmation of Einstein's general theory of relativity, the gyroscopes experienced measurable, minute changes in the direction of their spin as they were pulled by Earth's gravity." The probe's measurements came remarkably close to Einstein's projections, according to the findings published in the journal Physical Review Letters. The satellite, which wrapped up its data mission last year, was first envisioned in 1959. Leonard Schiff, head of Stanford's physics department, and George Pugh of the Defense Department, dreamed up a satellite that would orbit the Earth and test the notion. Everitt joined the project in 1962, followed by NASA in 1963. "Forty-one years later, the satellite was launched into orbit about 400 miles above Earth," NASA said. The technologies created in the development of the gravity probe have been used in making precise global position systems (GPS) and in gauging the background radiation of the universe. "That measurement is the underpinning of the 'big bang theory' and led to the Nobel Prize for NASA's John Mather," NASA said. Hundreds of university students and dozens of high schoolers have worked on the project, including famous names such as Sally Ride, who was the first American female astronaut in space, and Nobel Laureate Eric Cornell.
Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links The Physics of Time and Space
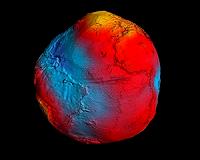 Earth's Gravity Revealed In Unprecedented Detail
Earth's Gravity Revealed In Unprecedented DetailParis, France (ESA) Apr 01, 2011 Paris, France (ESA) Apr 01, 2011 After just two years in orbit, ESA's GOCE satellite has gathered enough data to map Earth's gravity with unrivalled precision. Scientists now have access to the most accurate model of the 'geoid' ever produced to further our understanding of how Earth works. The new geoid was unveiled today at the Fourth International GOCE User Workshop hosted at the Techn ... read more |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2010 - SpaceDaily. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |