 |
Corvallis OR (SPX) Oct 11, 2010 Nanotechnology is about to emerge in the world of pesticides and pest control, and a range of new approaches are needed to understand the implications for public health, ensure that this is done safely, maximize the potential benefits and prevent possible risks, researchers say in a new report. In a study published in the International Journal of Occupational and Environmental Health, scientists from Oregon State University and the European Union outline six regulatory and educational issues that should be considered whenever nanoparticles are going to be used in pesticides. "If we do it right, it should be possible to design nanoparticles with safety as a primary consideration, so they can help create pesticides that work better or are actually safer," said Stacey Harper, an assistant professor of nanotoxicology at Oregon State University. Harper is a national leader in the safety and environmental impacts of this science that deals with particles so extraordinarily small they can have novel and useful characteristics. "Unlike some other applications of nanotechnology, which are further along in development, applications for pesticides are in their infancy," Harper said. "There are risks and a lot of uncertainties, however, so we need to understand exactly what's going on, what a particular nanoparticle might do, and work to eliminate use of any that do pose dangers." A program is already addressing that at OSU, as part of the Oregon Nanoscience and Microtechnologies Institute. The positive aspect of nanotechnology use with pesticides, researchers say, is that it might allow better control and delivery of active ingredients, less environmental drift, formulations that will most effectively reach the desired pest, and perhaps better protection for agricultural workers. "If you could use less pesticide and still accomplish the same goal, that's a concept worth pursuing," Harper said. But researchers need to be equally realistic about the dangers, she said. OSU labs have tested more than 200 nanomaterials, and very few posed any toxic concerns - but a few did. In one biomedical application, where nanoparticles were being studied as a better way to deliver a cancer drug, six out of 40 evoked a toxic response, most of which was linked to a specific surface chemistry that scientists now know to avoid. "The emergence of nanotechnology in the pesticide industry has already begun, this isn't just theoretical," said David Stone, an assistant professor in the OSU Department of Environmental and Molecular Toxicology. "But pesticides are already one of the most rigorously tested and regulated class of compounds, so we should be able to modify the existing infrastructure." One important concern, the researchers said, will be for manufacturers to disclose exactly what nanoparticles are involved in their products and what their characteristics are. Another issue is to ensure that compounds are tested in the same way humans would be exposed in the real world. "You can't use oral ingestion of a pesticide by a laboratory rat and assume that will tell you what happens when a human inhales the same substance," Stone said. "Exposure of the respiratory tract to nanoparticles is one of our key concerns, and we have to test compounds that way." Future regulations also need to acknowledge the additional level of uncertainty that will exist for nano-based pesticides with inadequate data, the scientists said in their report. Tests should be done using the commercial form of the pesticides, a health surveillance program should be initiated, and other public educational programs developed. Special assessments may also need to be developed for nanoparticle exposure to sensitive populations, such as infants, the elderly, or fetal exposure. And new methodologies may be required to understand nanoparticle effects, which are different from most traditional chemical tests. "These measures will require a coordinated effort between governmental, industry, academic and public entities to effectively deal with a revolutionary class of novel pesticides," the researchers concluded in their report.
Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links Oregon State University Farming Today - Suppliers and Technology
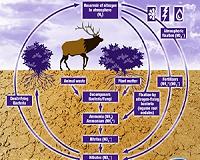 Human Activities Overload Ecosystems With Nitrogen
Human Activities Overload Ecosystems With NitrogenWashington DC (SPX) Oct 11, 2010 Humans are overloading ecosystems with nitrogen through the burning of fossil fuels and an increase in nitrogen-producing industrial and agricultural activities, according to a new study. While nitrogen is an element that is essential to life, it is an environmental scourge at high levels. According to the study, excess nitrogen that is contributed by human activities pollutes fresh waters ... read more |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2010 - SpaceDaily. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |