 |
Ann Arbor MI (SPX) Aug 29, 2007 A camper who chases a grizzly but won't risk unprotected sex. A sky diver afraid to stand up to the boss. New research shows that not all risk is created equal and people show a mixture of both risky and non-risky behaviors. The survey also shows that men are significantly riskier than women overall. The University of Michigan research refutes the standard theories of risk that group people as either risk-seeking or risk-avoiding, and suggests that we can have a mix of both risky and non-risky behavior depending on the type. The study appears in the journal Evolutionary Psychology. Daniel Kruger, a research scientist at the U-M School of Public Health, and colleagues X.T. Wang, University of South Dakota, and Andreas Wilke, UCLA, identified areas of risk taking (risk domains) based on the types of challenges that our ancestors faced during many thousands of years of human evolution. "People are complex," said Kruger. "Just because somebody seems to be a big risk taker in one area doesn't mean they will take risks in all areas." The types of risks identified include competition with other individuals; competition with other groups; mating and allocating resources for mate attraction; environmental risks (chasing a bear or skydiving); and fertility risks. The study showed that our tendencies for risk taking follow these different types of challenges. "It is remarkable not just that we were able to identify different areas of risk taking, but also that many of the challenges faced by our ancestors are similar to challenges we face in our modern world today," Kruger said. People surveyed for the study were least likely to take fertility risks, and most likely to take risks related to social status in one's group --- like standing up to one's boss. In all domains, men were significantly more risk taking than women. During human evolution, men competed for social status and resources in order to attract mates. Thus, this pattern is not surprising, Kruger said. The risks that threaten fertility function differently than the others, Kruger said. Other types of risk have a possible benefit in terms of survival and reproduction. But with fertility risks, there is just a threat to reproduction. They can only cause harm in the evolutionary sense since they would only hurt our ability to procreate. "Those were types of risks that weren't attractive to other people, those risks were the least likely to be taken, and people saw those risks as unattractive in a potential mate," Kruger said. Although in most parts of the world, threats from predators may be limited to those making wilderness expeditions, we still live in a world with complex challenges involving other individuals and material investments. The basic elements of our social environment have not changed; we just live on a much larger scale. Related Links University of Michigan University of Michigan School of Public Health All About Human Beings and How We Got To Be Here
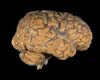 Washington DC (SPX) Aug 22, 2007
Washington DC (SPX) Aug 22, 2007The area of the brain responsible for self-control-where the decision not to do something occurs after thinking about doing it-is separate from the area associated with taking action, scientists say in the August 22 issue of The Journal of Neuroscience. "The results illuminate a very important aspect of the brain's control of behavior, the ability to hold off doing something after you've developed the intention to do it-one might call it 'free won't' as opposed to free will," says Martha Farah, PhD, of the University of Pennsylvania. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright Space.TV Corporation. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement, agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by Space.TV Corp on any Web page published or hosted by Space.TV Corp. Privacy Statement |