 |
Bethesda, MD (SPX) Jul 02, 2010 Sweet news for those looking for new antibiotics: A new research published in the July 2010 print edition of the FASEB Journal explains for the first time how honey kills bacteria. Specifically, the research shows that bees make a protein that they add to the honey, called defensin-1, which could one day be used to treat burns and skin infections and to develop new drugs that could combat antibiotic-resistant infections. "We have completely elucidated the molecular basis of the antibacterial activity of a single medical-grade honey, which contributes to the applicability of honey in medicine," said Sebastian A.J. Zaat, Ph.D., a researcher involved in the work from the Department of Medical Microbiology at the Academic Medical Center in Amsterdam. "Honey or isolated honey-derived components might be of great value for prevention and treatment of infections caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria." To make the discovery, Zaat and colleagues investigated the antibacterial activity of medical-grade honey in test tubes against a panel of antibiotic-resistant, disease-causing bacteria. They developed a method to selectively neutralize the known antibacterial factors in honey and determine their individual antibacterial contributions. Ultimately, researchers isolated the defensin-1 protein, which is part of the honey bee immune system and is added by bees to honey. After analysis, the scientists concluded that the vast majority of honey's antibacterial properties come from that protein. This information also sheds light on the inner workings of honey bee immune systems, which may one day help breeders create healthier and heartier honey bees. "We've known for millennia that honey can be good for what ails us, but we haven't known how it works," said Gerald Weissmann, M.D., Editor-in-Chief of the FASEB Journal, "Now that we've extracted a potent antibacterial ingredient from honey, we can make it still more effective and take the sting out of bacterial infections."
Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology Epidemics on Earth - Bird Flu, HIV/AIDS, Ebola
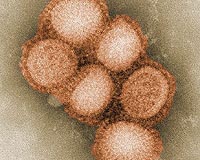 Hong Kong study promises new swine flu treatment
Hong Kong study promises new swine flu treatmentHong Kong (AFP) July 1, 2010 Hong Kong researchers have discovered a new way to treat patients suffering from swine flu, a report said Thursday, after the deadly virus killed more than 18,000 people worldwide in the past year. A joint study by the University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong Red Cross and the city's Hospital Authority has proven that plasma antibodies taken from recovered swine flu patients are an effective trea ... read more |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2010 - SpaceDaily. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |